中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (40): 6536-6541.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.40.024
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
三维有限元法分析脊柱保护器对人体胸腰段的支持与保护作用
何剑颖1,邓 亮1,李 晨1,吴小辉2,舒 勇3,董谢平1
- 1江西省人民医院骨科,江西省南昌市 330006;2景德镇市中医院骨科,江西省景德镇市 333000;3南昌大学一附院骨科,江西省南昌市 330006
Three-dimensional finite element analysis on the support and protection of spine protector for thoracic-lumbar vertebra
He Jian-ying1, Deng Liang1, Li Chen1, Wu Xiao-hui2, Shu Yong3, Dong Xie-ping1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Jingdezhen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jingdezhen 333000, Jiangxi Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
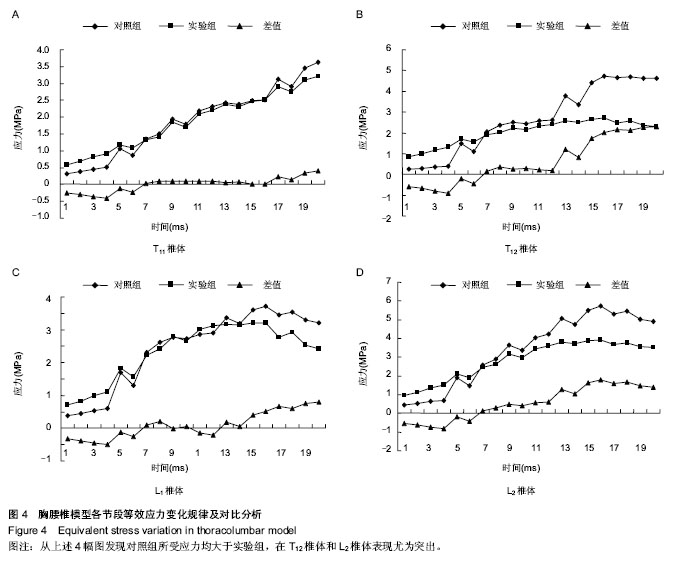
背景:人体脊柱保护器对预防人体胸腰段脊柱损伤有保护作用,新型动力性保护器的研发需要通过多种实验手段的验证。
目的:利用三维有限元法分析脊柱保护器在轴向载荷作用下对人体脊柱胸腰段的生物力学响应。
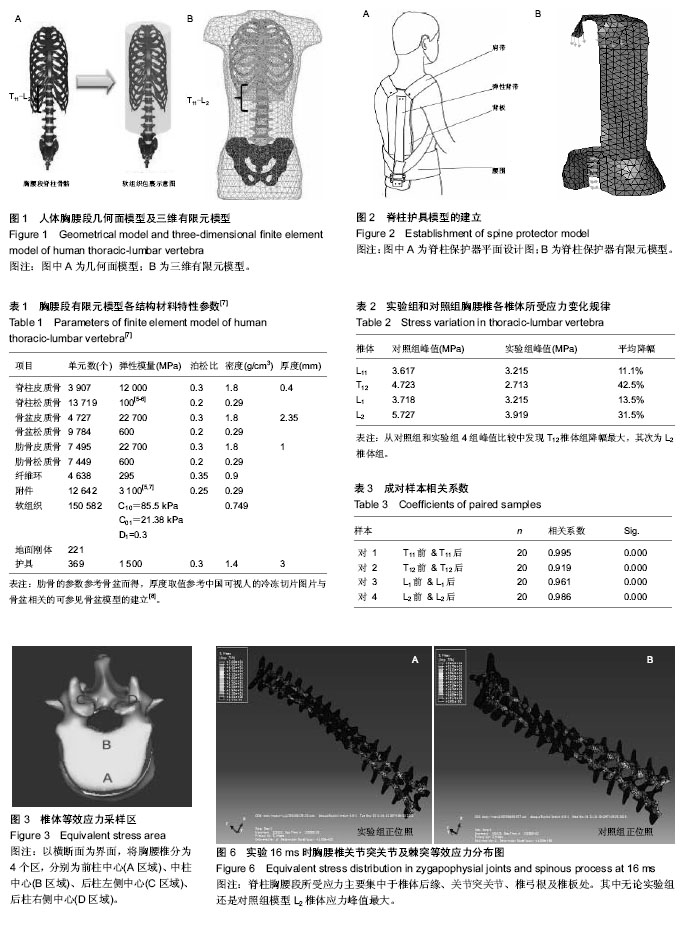
方法:从已建立的全脊柱三维有限元模型中截取胸腰段,将佩戴脊柱保护器的胸腰段模型设计为实验组,未佩戴脊柱保护器的胸腰段模型设计为对照组。给上述两组模型进行赋值、约束、加载、运算,获得目标单元的等效应力及应变。
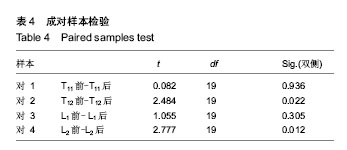
结果与结论:在垂直承载的两组胸腰段模型中,应力均集中于L2椎体的中、后柱。根据目标单元采集数据发现,实验组与对照组模型在16 ms时达到等效应力最大值,分别为3.919,5.727 MPa。统计分析得出T12与L2节段实验组与对照组等效应力比较,P均< 0.05,对照组所受应力均大于实验组,差异有显著性意义;而T11与L1节段实验组与对照组的等效应力比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。提示脊柱保护器可以明显减少垂直坠地时胸腰段椎体所受的应力,分担载荷,对胸腰段椎体具有保护支持作用。
中图分类号: